Care: Hermit Crab Nutrition by Kilimanjaro
Posted: Wed Mar 13, 2013 2:11 pm
This article was originaly published by Kilimanjaro on July 30, 2008. Some information may be out of date, but the overall information on hermit crab nutrition is sound. Questions about anything on this page - or questions about any food item - should be directed to the [Food & Water] section as a new topic.
Kilimanjaro's Guide to Hermit Crab Nutrition
First off, I would like to thank member blaze88 for helping me out on this guide. Blaze contributed a ton of information to incorporate into this guide for everyone to use and understand. Thank you so much for being a huge help!
Introduction to the Guide
I decided to formulate a guide to hermit crab nutrition due to the incomplete knowledge of hermit crab diet out there. Many new members are confused about what to feed their crabs and senior crabbers are also looking to provide a good diet for their land hermit crabs.
There is no complete guide to hermit crab nutrition (as this is not a complete guide) and there is no magic kibble that can possibly contain all of the foods that crabs need. This is because variety is the key to offering different nutrients that the hermit crab has a need for. New foods should always be incorporated into a land hermit crab's diet.
The guide that is made up here is broken down into different nutrients and different food groups that crabs need. In the nutrients section I tried to identify the nutrient, explain what it does in the crab's body, and then give examples of foods that are high in this particular nutrient. In the food groups section, I tried to identify the food group, explain why it is important, and then give examples of foods that are in this group.
Additionally, the guide provides a list of favorite foods, a section regarding molting and feeding, and a food warning section.
Without further adieu, I present Kilimanjaro's Guide to Hermit Crab Nutrition!
Key Nutrients
There are many key nutrients needed in a crustacean's diet. Protein is a particularly important nutrient that many crabbers do not offer enough of. It is imperative to get a source of protein in your hermit crab's diet every night (or feeding period).
The key nutrients are listed in alphabetical order.
Astaxanthin
Definition - a strong pigment molecule that is usually found in rich red foods.
Function - enhances color in land hermit crab's exoskeleton and aids in keeping organ systems and bodily functions healthy.
Foods - krill, plankton, red seaweeds, shrimp
Beta Carotene
Definition - an orange and red pigment molecule that is found in brightly-colored foods.
Function - enhances red and orange color in hermit crab's exoskeleton and is processed into Vitamin A in a hermit crab's body
Foods - apricots, bell pepper (red, orange, and yellow), blueberry, broccoli, cantaloupe, carrot, chard, cilantro (raw), collard greens, dandelion greens (raw), lettuce (dark), mango, microalgaes, papaya, parsley (raw), passionfruit, peaches, peas, persimmon, pineapple, pumpkin, snap beans (raw), spinach, spirulina, squash, seaweeds, sweet potato
Calcium
Definition - a soft-grey alkaline earth metal (Ca)
Function - aids in exoskeletal health and works as a signal in many cellular functions, including brain function
Foods - amaranth, blackstrap molasses, broccoli, cuttlebone, eggshell, exoskeleton, figs, microalgaes, nuts, okra, orange, oyster shell, quinoa, seaweeds, seeds, insects
Carbohydrates
Definition - a biomolecule that is processed into sugar in the bodies of all living things
Function - store and transport short-term energy and make up part of the chitin in the exoskeleton
Foods - fruit (assorted), grains, honey, microalgaes, noodles, quinoa, rice, seaweed, vegetables (assorted and especially dried), wheat germ
Cellulose
Definition - a compound making up many tissues and cell walls in plants
Function - provides fiber in diet and also contains many color-enhancing molecules
Foods - fruits, tree bark, tree leaves, vegetables
Fats (Lipids)
Definition - molecules that store energy and are found in solid (fat) or liquid (oil) forms
Function - used to make cell membranes and dissolve certain vitamins
Foods - almonds, canola oil*, coconut, coconut oil*, egg yolks, meat fat, olive oil*, palm oil*, pumpkin seed oil*, pumpkin seeds, salmon, sunflower seed oil*, sunflower seeds, walnuts
*when picking an oil, cold-pressed oils are the best choice
Other Carotenoids
Definition - molecules that enhance color and reflect different wavelengths of light
Function - enhance color in the hermit crab exoskeleton and aid in bodily functions and keeping organ systems healthy
Foods - apricot, blueberry, carrot, collard greens, egg yolk, guava, kale, mango, pink grapefruit, salmon, shellfish, spinach, squash, sweet potato, tomato
Phytonutrients
Definition - small compounds and molecules that are important in a diet, but too small and too insignificant to research and understand
Function - keeps bodily functions and organ systems healthy
Foods - any nutritional food
Protein
Definition - a compound made up of many smaller amino acids
Function - keeps exoskeleton, muscular, and other bodily systems healthy, and allows the body to process carbohydrates and lipids
Foods - alfalfa hay, broccoli, crab, egg whites, flax seed, freeze-dried bloodworm, freeze-dried plankton, freeze-dried shrimp, crickets, mealworms, game meat, kale, lean beef, lean chicken, lean turkey, lentil, millet, rice, salmon, shrimp, snap peas, soy beans, spinach, tuna, wheat germ
Tannin
Definition - a pigment molecule that is found in fibrous foods
Function - enhances color in land hermit crabs and keeps bodily systems healthy
Foods - roots, tree bark, tree leaves
Vitamins
Definition - a compound that cannot be synthesized by an organism and thus is required by consuming
Function - keeping bodily systems, appearance, and organ systems healthy
Foods - various fruits, vegetables, and other food groups
Zeaxanthin
Definition - a carotenoid found in various foods
Function - enhances color of the exoskeleton and also aids in bodily functions
Foods - avocado, bell pepper (orange and red), broccoli, brussel sprouts, carrot, cilantro, collards, corn (yellow), corn meal, dandelion greens, egg yolk, grape leaves, lettuce (romaine), papaya, parsley, peas, raspberry, spirulina
Key Food Groups
After much talk and figuring, blaze88 and I have managed to come up with seven different food groups and foods that are in each group. The food groups have been arranged into a hermit crab food pyramid.
Please keep in mind that the pyramid below is a guide to feed. By no means do you have to follow the schedule exactly. These guidelines are scientifically backed by the book Crustacean Nutrition (reference below).
If your land hermit crabs do not eat all of the food based on the schedule, do not fret. Crabs can be picky eaters and have an ability to seek out the nutrients they are looking for. By feeding all of the food groups on the pyramid when required, you are verifying that you are giving your land hermit crab access to all the nutrients they need.
The hermit crab food pyramid is very user-friendly and easy to read. The foods on the bottom are most important the foods on the top are less important. However, all of the food groups are imperative to hermit crab health. The key on the right-hand side describes how many times to feed this food group a week. When the pyramid level is broken in half, you can choose either food group. The larger the section, the more important it is.
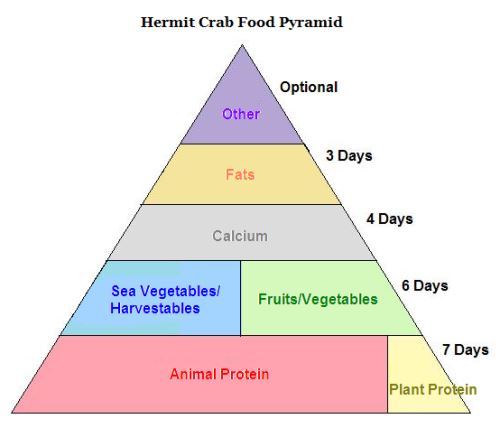
I have decided to explain the food groups in order of importance.
Animal Protein & Plant Protein
This group is most important to a land hermit crab's diet. Foods high in protein should be fed every day so the land hermit crab can access the correct amino acids it requires. Animal proteins are more important than plant proteins, but plant proteins can be fed along with animal proteins.
Foods of the animal protein group include: crab, egg whites, freeze-dried bloodworm, freeze-dried plankton, earthworm, freeze-dried shrimp, cricket, mealworm, game meat, lean beef, lean chicken, lean turkey, salmon, shrimp, tuna
Food of the plant protein group include: alfalfa hay, broccoli, corn, flax seed, kale, lentil, millet, rice, snap peas, soy beans, spinach, wheat germ
Sea Vegetables & Harvestables and Fruits & Vegetables
This group is important to a land hermit crab's diet because it is diverse in many different nutrients. Sea vegetables are high in many necessary minerals and harvestable foods are high in many other nutrients. Fruits and vegetables come along with many different types of vitamins and healthy nutrients. It is important to offer a variety of foods from this level of the food pyramid.
Foods of the sea vegetables group include: algae, kelp, nori, spirulina, wakame, various algae, various seaweeds
Foods of the harvestables group include: (see Harvestables list)
Foods of the fruits and vegetables group include: apple, avocado, banana, blackberry, blueberry, carrot, celery, cherry, coconut, fig, grape, guava, kiwi, lettuce (dark varieties), mango, orange, peach, pear, pineapple, plum, pomegranate, potato, pumpkin, raspberry, squash, tomato, various other fruits, various other vegetables
Calcium
This group is important in a hermit crab's diet because calcium is an important mineral that helps in exoskeletal health and other bodily functions. Calcium should be fed often and comes in a variety of different forms. Calcium can be fed in dairy forms, although some speculate that crabs do not absorb dairy calcium as well as hard forms. Any greens containing calcium should be quickly cooked in order to disable the oxalic acids, which can prevent calcium absorption. Care should be taken to pick foods with calcium that are also low in oxalic acids and phosphorus.
Foods of the calcium group include: amaranth, beans, blackstrap molasses, broccoli, cuttlebone, dark greens (cooked), eggshell, exoskeleton, figs, microalgaes, nuts, okra, orange, oyster shell, quinoa, reptile calcium supplement, seaweeds, seeds, insects
Fats (Lipids)
This group is important in a hermit crab's diet because it can help in molting and also stores energy. Fats are found in plant and animal forms. Fats are not needed in as high amount as protein, which is why when crabs are feeding on an animal protein source it should be lean. There are some beneficial fats and oils in a hermit crab's diet. The two fatty acids that hermit crabs require are n-3 and n-6, which are found in oils and some other sources of fat.
Foods of the fats group include: almonds, canola oil, coconut, coconut oil, egg yolks, meat fat, olive oil, palm oil, pumpkin seed oil, pumpkin seeds, salmon, sunflower seed oil, sunflower seeds, walnuts
Other
This group is not as important as the other groups, and, in fact, is optional. These foods can be chosen to fed or they can be disregarded. The foods in this group can have beneficial factors and nutrients. This group is very diverse and contains some of the favorite foods of land hermit crabs. Some of these are great healthy treats and others, like vinegar, help with illnesses like post-purchase syndrome (PPS).
Foods of the other group include: blackstrap molasses, cuttlebone, earthworm castings, eggshell, honey, mineral supplements, oyster shell, saltwater, vinegar (with mother)
Hermit Crab Nutrition and the Molting Cycle
Pre-molt and post-molt crabs require different foods as far as regular hermit crab nutrition goes. Before molts, many land hermit crabs are known to eat a lot to gather enough energy and nutrients to sustain themselves throughout molts. Additionally, most land hermit crabs will eat a lot to regain nutrients so they can get back to their normal selves.
What to Feed Pre-Molt Land Hermit Crabs
It is important to feed pre-molt hermit crabs foods rich in different nutrients. Protein and calcium are two of the most important nutrients you can feed your land hermit crabs when they are pre-molt.
Some people have noted that oils help land hermit crabs shed their exoskeleton. Feeding different oils (coconut, red palm, or olive) can be beneficial to a pre-molt hermit crab.
What to Feed Post-Molt Land Hermit Crabs
Post-molt land hermit crabs should be fed a various diet with foods rich in different vitamins and other beneficial nutrients. You should try to feed the healthiest foods to your post-molt crabs for a week or two in order to have them regain their nutrient levels and they start to metabolize food easier.
But What Happens When They're Underground?
Land hermit crabs eat a lot prior to a molt so they are able to sustain themselves. The molt sac does not contain many nutrients, but water. The water pressure helps them break their exoskeleton during the molt.
Because they do not eat when they are molting (besides their exoskeleton to regain nutrients for the new one), good foods should be fed before molts and afterwards.
Reference:
Hermit Crab Food Favorites
Hermit crabs enjoy certain foods that are high in nutrients and can also satisfy them with a certain taste. Some of the hermit crab favorite foods I have collected came from the forum. I have decided to post the most popular foods.
Bloodworms (freeze-dried)
Blueberries
Chicken bone marrow
Coconut
Cuttlebone
Earthworm castings
Krill (frozen & thawed or freeze-dried)
Mango
Millet
Oak leaves
Papaya
Peanut butter (organic)
Persimmon
Pineapple
Popcorn (no butter or salt)
Rolled oats
Shrimp (whole)
Wheat germ
Hermit Crab Food Warnings
Although there are many foods that are safe for hermit crabs, there are some unsafe foods and some food warnings.
Food Warning #1: Unsafe Foods
To view both safe and unsafe foods, please visit our Guide to Safe and Unsafe Foods. Keep in mind that the safe food list is not a complete list, and more foods are always being added.
Food Warning #2: Oxalic Acid in Greens
Many greens have oxalic acid inside of them. Oxalic acid binds to calcium and makes it unprocessable by reptiles, humans and other mammals. Foods high in oxalic acids should be avoided or fed sparingly as we do not know the affects on crustaceans.
Food Warning #3: Preservatives in Commercial Foods
There are many preservatives in commercial foods for land hermit crabs. Please refer to our Guide about Commercial Foods to learn more about additives and harmful substances.
The preservatives and harmful ingredients that everyone should be looking out for in commercial foods are artificial color, by-products, copper sulphate/sulfate, ethoxyquin, ferrous sulfate, foods containing "meal", magnesium oxide, menadione, propylene glycol, sodium chloride, zeolite, zinc oxide
There are many natural kibbles that can be purchased. Please see our Shopping Links for stores that sell safe hermit crab foods.
Food Warning #4: Pesticides in Foods
Most of the fruits and vegetables we eat today have been sprayed with pesticides in order to produce more food to feed the growing population. Because pesticides and insecticides are designed to target the exoskeleton of insects, it is possible that pesticides can be harmful to hermit crabs because they also have an exoskeleton.
Many crabbers opt to buy natural and organic products in order to cut out pesticide consumption. Berries and thin skinned foods have the highest amount of pesticides in them and many crabbers make sure to buy these organic. Foods with thick peels or rinds absorb most of the pesticides in the skin and the skin should not be fed unless it is organic.
Conclusion
I would like to mention that this is not a complete reference to hermit crab nutrition, but simply a guide. Hermit crab nutrition is constantly changing and more is learned each day.
I am completely open to editing this guide. All comments, suggestions, questions, and criticisms are welcome to be posted. I value everyone's opinion and I would love to hear what you all honestly think.
[Edited by Admin to update links and some info March 2013]
Kilimanjaro's Guide to Hermit Crab Nutrition
First off, I would like to thank member blaze88 for helping me out on this guide. Blaze contributed a ton of information to incorporate into this guide for everyone to use and understand. Thank you so much for being a huge help!
Introduction to the Guide
I decided to formulate a guide to hermit crab nutrition due to the incomplete knowledge of hermit crab diet out there. Many new members are confused about what to feed their crabs and senior crabbers are also looking to provide a good diet for their land hermit crabs.
There is no complete guide to hermit crab nutrition (as this is not a complete guide) and there is no magic kibble that can possibly contain all of the foods that crabs need. This is because variety is the key to offering different nutrients that the hermit crab has a need for. New foods should always be incorporated into a land hermit crab's diet.
The guide that is made up here is broken down into different nutrients and different food groups that crabs need. In the nutrients section I tried to identify the nutrient, explain what it does in the crab's body, and then give examples of foods that are high in this particular nutrient. In the food groups section, I tried to identify the food group, explain why it is important, and then give examples of foods that are in this group.
Additionally, the guide provides a list of favorite foods, a section regarding molting and feeding, and a food warning section.
Without further adieu, I present Kilimanjaro's Guide to Hermit Crab Nutrition!
Key Nutrients
There are many key nutrients needed in a crustacean's diet. Protein is a particularly important nutrient that many crabbers do not offer enough of. It is imperative to get a source of protein in your hermit crab's diet every night (or feeding period).
The key nutrients are listed in alphabetical order.
Astaxanthin
Definition - a strong pigment molecule that is usually found in rich red foods.
Function - enhances color in land hermit crab's exoskeleton and aids in keeping organ systems and bodily functions healthy.
Foods - krill, plankton, red seaweeds, shrimp
Beta Carotene
Definition - an orange and red pigment molecule that is found in brightly-colored foods.
Function - enhances red and orange color in hermit crab's exoskeleton and is processed into Vitamin A in a hermit crab's body
Foods - apricots, bell pepper (red, orange, and yellow), blueberry, broccoli, cantaloupe, carrot, chard, cilantro (raw), collard greens, dandelion greens (raw), lettuce (dark), mango, microalgaes, papaya, parsley (raw), passionfruit, peaches, peas, persimmon, pineapple, pumpkin, snap beans (raw), spinach, spirulina, squash, seaweeds, sweet potato
Calcium
Definition - a soft-grey alkaline earth metal (Ca)
Function - aids in exoskeletal health and works as a signal in many cellular functions, including brain function
Foods - amaranth, blackstrap molasses, broccoli, cuttlebone, eggshell, exoskeleton, figs, microalgaes, nuts, okra, orange, oyster shell, quinoa, seaweeds, seeds, insects
Carbohydrates
Definition - a biomolecule that is processed into sugar in the bodies of all living things
Function - store and transport short-term energy and make up part of the chitin in the exoskeleton
Foods - fruit (assorted), grains, honey, microalgaes, noodles, quinoa, rice, seaweed, vegetables (assorted and especially dried), wheat germ
Cellulose
Definition - a compound making up many tissues and cell walls in plants
Function - provides fiber in diet and also contains many color-enhancing molecules
Foods - fruits, tree bark, tree leaves, vegetables
Fats (Lipids)
Definition - molecules that store energy and are found in solid (fat) or liquid (oil) forms
Function - used to make cell membranes and dissolve certain vitamins
Foods - almonds, canola oil*, coconut, coconut oil*, egg yolks, meat fat, olive oil*, palm oil*, pumpkin seed oil*, pumpkin seeds, salmon, sunflower seed oil*, sunflower seeds, walnuts
*when picking an oil, cold-pressed oils are the best choice
Other Carotenoids
Definition - molecules that enhance color and reflect different wavelengths of light
Function - enhance color in the hermit crab exoskeleton and aid in bodily functions and keeping organ systems healthy
Foods - apricot, blueberry, carrot, collard greens, egg yolk, guava, kale, mango, pink grapefruit, salmon, shellfish, spinach, squash, sweet potato, tomato
Phytonutrients
Definition - small compounds and molecules that are important in a diet, but too small and too insignificant to research and understand
Function - keeps bodily functions and organ systems healthy
Foods - any nutritional food
Protein
Definition - a compound made up of many smaller amino acids
Function - keeps exoskeleton, muscular, and other bodily systems healthy, and allows the body to process carbohydrates and lipids
Foods - alfalfa hay, broccoli, crab, egg whites, flax seed, freeze-dried bloodworm, freeze-dried plankton, freeze-dried shrimp, crickets, mealworms, game meat, kale, lean beef, lean chicken, lean turkey, lentil, millet, rice, salmon, shrimp, snap peas, soy beans, spinach, tuna, wheat germ
Tannin
Definition - a pigment molecule that is found in fibrous foods
Function - enhances color in land hermit crabs and keeps bodily systems healthy
Foods - roots, tree bark, tree leaves
Vitamins
Definition - a compound that cannot be synthesized by an organism and thus is required by consuming
Function - keeping bodily systems, appearance, and organ systems healthy
Foods - various fruits, vegetables, and other food groups
Zeaxanthin
Definition - a carotenoid found in various foods
Function - enhances color of the exoskeleton and also aids in bodily functions
Foods - avocado, bell pepper (orange and red), broccoli, brussel sprouts, carrot, cilantro, collards, corn (yellow), corn meal, dandelion greens, egg yolk, grape leaves, lettuce (romaine), papaya, parsley, peas, raspberry, spirulina
Key Food Groups
After much talk and figuring, blaze88 and I have managed to come up with seven different food groups and foods that are in each group. The food groups have been arranged into a hermit crab food pyramid.
Please keep in mind that the pyramid below is a guide to feed. By no means do you have to follow the schedule exactly. These guidelines are scientifically backed by the book Crustacean Nutrition (reference below).
If your land hermit crabs do not eat all of the food based on the schedule, do not fret. Crabs can be picky eaters and have an ability to seek out the nutrients they are looking for. By feeding all of the food groups on the pyramid when required, you are verifying that you are giving your land hermit crab access to all the nutrients they need.
The hermit crab food pyramid is very user-friendly and easy to read. The foods on the bottom are most important the foods on the top are less important. However, all of the food groups are imperative to hermit crab health. The key on the right-hand side describes how many times to feed this food group a week. When the pyramid level is broken in half, you can choose either food group. The larger the section, the more important it is.

I have decided to explain the food groups in order of importance.
Animal Protein & Plant Protein
This group is most important to a land hermit crab's diet. Foods high in protein should be fed every day so the land hermit crab can access the correct amino acids it requires. Animal proteins are more important than plant proteins, but plant proteins can be fed along with animal proteins.
Foods of the animal protein group include: crab, egg whites, freeze-dried bloodworm, freeze-dried plankton, earthworm, freeze-dried shrimp, cricket, mealworm, game meat, lean beef, lean chicken, lean turkey, salmon, shrimp, tuna
Food of the plant protein group include: alfalfa hay, broccoli, corn, flax seed, kale, lentil, millet, rice, snap peas, soy beans, spinach, wheat germ
Sea Vegetables & Harvestables and Fruits & Vegetables
This group is important to a land hermit crab's diet because it is diverse in many different nutrients. Sea vegetables are high in many necessary minerals and harvestable foods are high in many other nutrients. Fruits and vegetables come along with many different types of vitamins and healthy nutrients. It is important to offer a variety of foods from this level of the food pyramid.
Foods of the sea vegetables group include: algae, kelp, nori, spirulina, wakame, various algae, various seaweeds
Foods of the harvestables group include: (see Harvestables list)
Foods of the fruits and vegetables group include: apple, avocado, banana, blackberry, blueberry, carrot, celery, cherry, coconut, fig, grape, guava, kiwi, lettuce (dark varieties), mango, orange, peach, pear, pineapple, plum, pomegranate, potato, pumpkin, raspberry, squash, tomato, various other fruits, various other vegetables
Calcium
This group is important in a hermit crab's diet because calcium is an important mineral that helps in exoskeletal health and other bodily functions. Calcium should be fed often and comes in a variety of different forms. Calcium can be fed in dairy forms, although some speculate that crabs do not absorb dairy calcium as well as hard forms. Any greens containing calcium should be quickly cooked in order to disable the oxalic acids, which can prevent calcium absorption. Care should be taken to pick foods with calcium that are also low in oxalic acids and phosphorus.
Foods of the calcium group include: amaranth, beans, blackstrap molasses, broccoli, cuttlebone, dark greens (cooked), eggshell, exoskeleton, figs, microalgaes, nuts, okra, orange, oyster shell, quinoa, reptile calcium supplement, seaweeds, seeds, insects
Fats (Lipids)
This group is important in a hermit crab's diet because it can help in molting and also stores energy. Fats are found in plant and animal forms. Fats are not needed in as high amount as protein, which is why when crabs are feeding on an animal protein source it should be lean. There are some beneficial fats and oils in a hermit crab's diet. The two fatty acids that hermit crabs require are n-3 and n-6, which are found in oils and some other sources of fat.
Foods of the fats group include: almonds, canola oil, coconut, coconut oil, egg yolks, meat fat, olive oil, palm oil, pumpkin seed oil, pumpkin seeds, salmon, sunflower seed oil, sunflower seeds, walnuts
Other
This group is not as important as the other groups, and, in fact, is optional. These foods can be chosen to fed or they can be disregarded. The foods in this group can have beneficial factors and nutrients. This group is very diverse and contains some of the favorite foods of land hermit crabs. Some of these are great healthy treats and others, like vinegar, help with illnesses like post-purchase syndrome (PPS).
Foods of the other group include: blackstrap molasses, cuttlebone, earthworm castings, eggshell, honey, mineral supplements, oyster shell, saltwater, vinegar (with mother)
Hermit Crab Nutrition and the Molting Cycle
Pre-molt and post-molt crabs require different foods as far as regular hermit crab nutrition goes. Before molts, many land hermit crabs are known to eat a lot to gather enough energy and nutrients to sustain themselves throughout molts. Additionally, most land hermit crabs will eat a lot to regain nutrients so they can get back to their normal selves.
What to Feed Pre-Molt Land Hermit Crabs
It is important to feed pre-molt hermit crabs foods rich in different nutrients. Protein and calcium are two of the most important nutrients you can feed your land hermit crabs when they are pre-molt.
Some people have noted that oils help land hermit crabs shed their exoskeleton. Feeding different oils (coconut, red palm, or olive) can be beneficial to a pre-molt hermit crab.
What to Feed Post-Molt Land Hermit Crabs
Post-molt land hermit crabs should be fed a various diet with foods rich in different vitamins and other beneficial nutrients. You should try to feed the healthiest foods to your post-molt crabs for a week or two in order to have them regain their nutrient levels and they start to metabolize food easier.
But What Happens When They're Underground?
Land hermit crabs eat a lot prior to a molt so they are able to sustain themselves. The molt sac does not contain many nutrients, but water. The water pressure helps them break their exoskeleton during the molt.
Because they do not eat when they are molting (besides their exoskeleton to regain nutrients for the new one), good foods should be fed before molts and afterwards.
Reference:
Crustacean Nutrition
By Louis R. D'Abramo, Douglas E. Conklin, Dean M. Akiyama, International Working Group on Crustacean Nutrition, World Aquaculture Society
Published by World Aquaculture Society, 1997
ISBN 1888807008, 9781888807004
587 pages
Hermit Crab Food Favorites
Hermit crabs enjoy certain foods that are high in nutrients and can also satisfy them with a certain taste. Some of the hermit crab favorite foods I have collected came from the forum. I have decided to post the most popular foods.
Bloodworms (freeze-dried)
Blueberries
Chicken bone marrow
Coconut
Cuttlebone
Earthworm castings
Krill (frozen & thawed or freeze-dried)
Mango
Millet
Oak leaves
Papaya
Peanut butter (organic)
Persimmon
Pineapple
Popcorn (no butter or salt)
Rolled oats
Shrimp (whole)
Wheat germ
Hermit Crab Food Warnings
Although there are many foods that are safe for hermit crabs, there are some unsafe foods and some food warnings.
Food Warning #1: Unsafe Foods
To view both safe and unsafe foods, please visit our Guide to Safe and Unsafe Foods. Keep in mind that the safe food list is not a complete list, and more foods are always being added.
Food Warning #2: Oxalic Acid in Greens
Many greens have oxalic acid inside of them. Oxalic acid binds to calcium and makes it unprocessable by reptiles, humans and other mammals. Foods high in oxalic acids should be avoided or fed sparingly as we do not know the affects on crustaceans.
Food Warning #3: Preservatives in Commercial Foods
There are many preservatives in commercial foods for land hermit crabs. Please refer to our Guide about Commercial Foods to learn more about additives and harmful substances.
The preservatives and harmful ingredients that everyone should be looking out for in commercial foods are artificial color, by-products, copper sulphate/sulfate, ethoxyquin, ferrous sulfate, foods containing "meal", magnesium oxide, menadione, propylene glycol, sodium chloride, zeolite, zinc oxide
There are many natural kibbles that can be purchased. Please see our Shopping Links for stores that sell safe hermit crab foods.
Food Warning #4: Pesticides in Foods
Most of the fruits and vegetables we eat today have been sprayed with pesticides in order to produce more food to feed the growing population. Because pesticides and insecticides are designed to target the exoskeleton of insects, it is possible that pesticides can be harmful to hermit crabs because they also have an exoskeleton.
Many crabbers opt to buy natural and organic products in order to cut out pesticide consumption. Berries and thin skinned foods have the highest amount of pesticides in them and many crabbers make sure to buy these organic. Foods with thick peels or rinds absorb most of the pesticides in the skin and the skin should not be fed unless it is organic.
Conclusion
I would like to mention that this is not a complete reference to hermit crab nutrition, but simply a guide. Hermit crab nutrition is constantly changing and more is learned each day.
I am completely open to editing this guide. All comments, suggestions, questions, and criticisms are welcome to be posted. I value everyone's opinion and I would love to hear what you all honestly think.
[Edited by Admin to update links and some info March 2013]